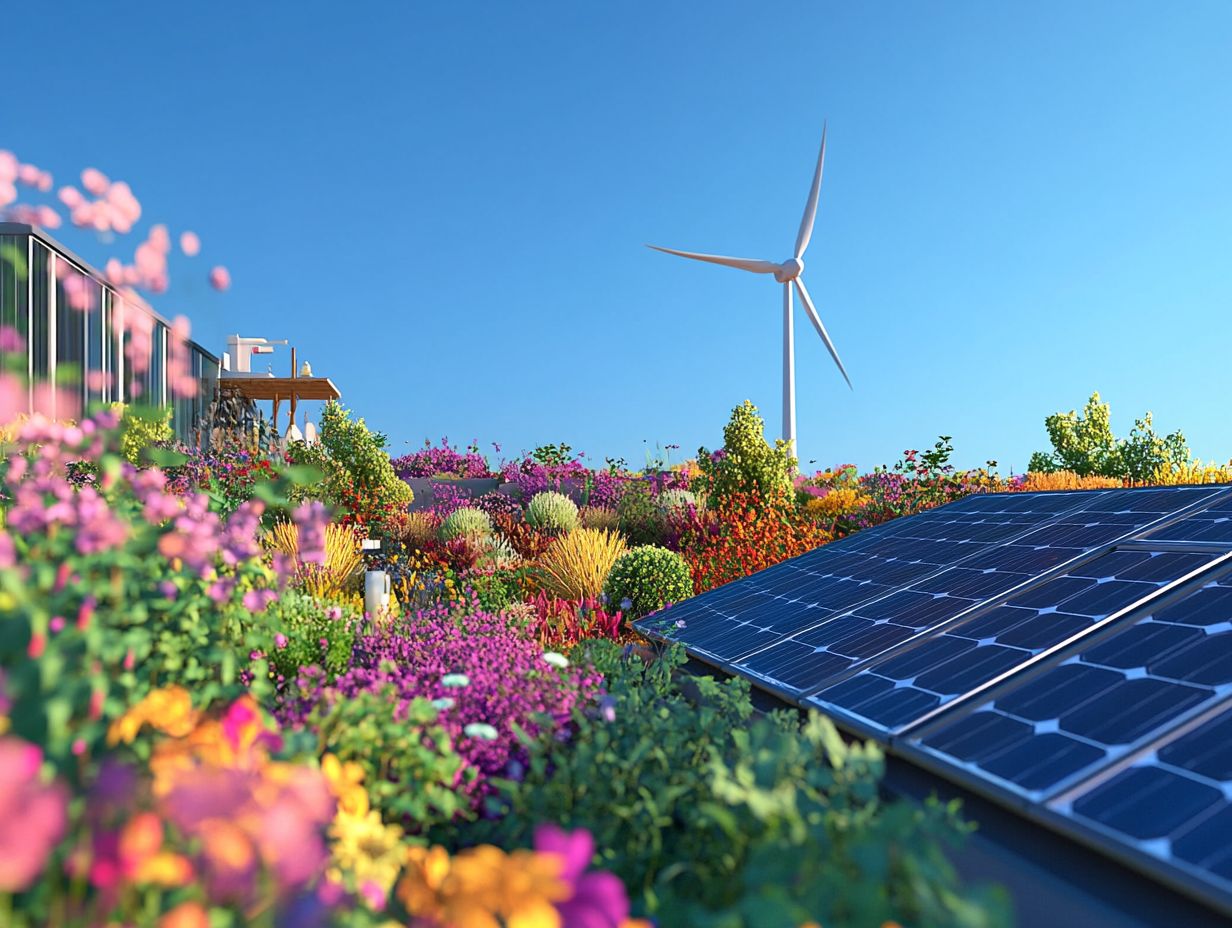
In an era marked by climate change and a growing demand for sustainable energy solutions, photovoltaic (PV) systems have emerged as a beacon of hope. These innovative technologies, which convert sunlight directly into electricity, are transforming the energy landscape and paving the way for a cleaner, more sustainable future. As we explore the rise of photovoltaic systems, we’ll delve into their technological advancements, economic viability, environmental benefits, and the critical role they play in the global transition to renewable energy.
The Technology Behind Photovoltaics
Photovoltaic systems operate on a relatively simple principle: they convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. At the heart of these systems are solar cells, typically made from silicon, which absorb photons from sunlight. When these photons strike the silicon, they knock electrons loose, generating an electric current. This process is facilitated by the structure of the solar cells, which creates an electric field that directs the flow of these free electrons.
Over the past few decades, advancements in technology have significantly improved the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of solar cells. Innovations such as bifacial solar panels, which capture sunlight from both sides, and thin-film solar technologies, which utilize less material while still generating substantial power, have broadened the applications and appeal of PV systems.
Economic Viability
One of the most remarkable aspects of the rise of photovoltaic systems is their declining cost. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the global weighted average cost of electricity from solar photovoltaics fell by 89% between 2010 and 2020. This dramatic reduction has made solar energy one of the most affordable sources of electricity in many parts of the world, prompting both residential and commercial investments.
Government incentives, such as tax credits, grants, and subsidies, have further accelerated the adoption of solar technology. Additionally, the rise of innovative financing models, including power purchase agreements (PPAs) and community solar programs, has allowed even those without suitable rooftops to benefit from solar energy.
As countries strive to meet their climate goals, the economic viability of PV systems becomes even more critical. The growth of solar jobs, which reached over 3.3 million worldwide in 2021, further underscores the industry’s potential to contribute to economic recovery and job creation.
Environmental Benefits
The environmental advantages of photovoltaic systems are clear. By harnessing the sun’s energy, PV systems produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, significantly reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional fossil fuels. Furthermore, solar energy is abundant and renewable, making it a sustainable alternative that can help mitigate climate change.
Beyond reducing greenhouse gas emissions, solar energy can also play a vital role in water conservation. Unlike traditional power generation methods, which often require substantial water for cooling, PV systems use minimal water, making them an ideal solution in arid regions.
Moreover, as the technology continues to evolve, efforts to improve recyclability and reduce the environmental impact of manufacturing processes are gaining momentum. Innovations in recycling techniques for end-of-life solar panels are being developed, ensuring that the industry moves toward a circular economy.
The Role of PV Systems in Global Energy Transition
Globally, the transition to renewable energy sources is essential for achieving energy security and sustainability. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar power could become the largest source of electricity by 2050, accounting for nearly 30% of the world’s energy needs. This shift is driven not only by the need to combat climate change but also by the desire for energy independence and resilience.
Countries across the globe are investing in large-scale solar farms, integrating photovoltaic systems into their energy grids, and encouraging residential solar installations. From the sun-drenched deserts of the Middle East to the rooftops of urban cities, photovoltaic systems are becoming integral components of energy policy and planning.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While the rise of photovoltaic systems brings numerous benefits, challenges remain. Issues such as land use for large solar farms, the need for energy storage solutions to manage intermittent supply, and the environmental impact of manufacturing materials must be addressed. However, ongoing research and development are aimed at overcoming these obstacles.
The future of photovoltaic systems looks promising. With continuous technological advancements, increasing public and private investments, and strong policy support, the solar industry is poised for exponential growth. As we strive for a sustainable energy future, the transition to photovoltaic systems will undoubtedly play a crucial role in illuminating the path forward.
Conclusion
The rise of photovoltaic systems marks a pivotal moment in the renewable energy landscape. By harnessing the power of the sun, these technologies offer a sustainable solution to some of the most pressing challenges of our time. As we look ahead, embracing and promoting the use of photovoltaic systems will be essential in our collective journey toward a greener, cleaner, and more sustainable world. The future is bright, and with solar energy leading the way, we are well on our path to illuminating a cleaner tomorrow.